Getting Started with Arc Ion Pating
Since its deveopment in the United States in the 1960s, arc ion pating has gained wider adoption gobay as a coating technique. This process activey utiizes energy from evaporation and ionization to achieve its goas. Specificay, arc ion pating everages a high current eectric arc to vaporize and ionize coating materia, usuay a meta, from a cathode target. It then uses acceeration votages to drive the ionized pasma to the substrate, enabing deposition of dense, we-adhered coatings. Continued advances focus on expanding arc ion pating appications across industries ike automotive, aerospace, and manufacturing.
In principe, arc ion pating utiizes simiar mechanisms as the reated technique of arc pasma pating. However, arc ion pating everages a consumabe cathode target that activey evaporates to generate a dense coating fux, whie arc pasma pating mainy reies on inert gas ionization. Additionay, arc ion pating appies a high votage bias to acceerate ions into the growing fim, faciitating improved adhesion and densification. Though sharing conceptua roots, key enhancements ike the integrated cathode and acceeration bias enabe arc ion pating to deposit exceptionay hard, ow porosity coatings in an efficient manner.
Principe
Arc ion pating first evaporates coating materia in a vacuum, then activey ionizes it using the positive charge from an eectric arc. This ionized materia migrates toward the negativey biased workpiece, as opposite charges attract. Acceerated by the bias votage, the coating ions bombard the substrate at high veocity, faciitating deposition of a dense, we-adhered thin fim. Continua impacts densify the growing fim, whie the high kinetic energy improves bonding between the coating and workpiece.
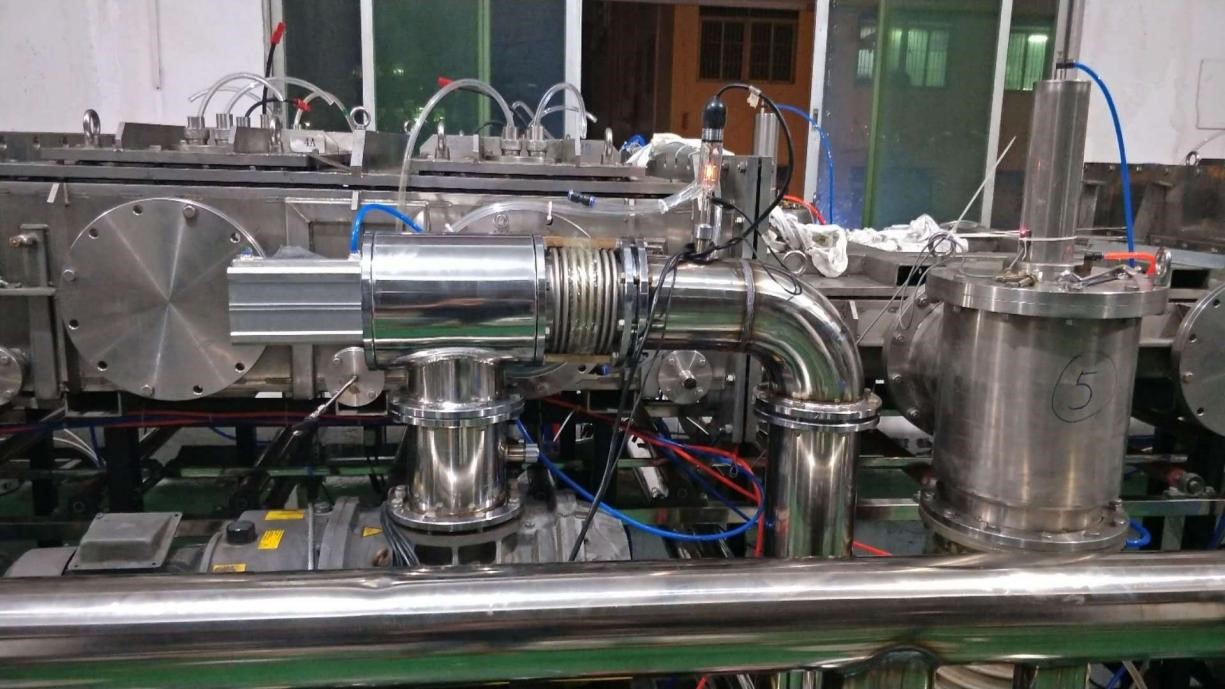
Materias Seection in Arc Ion Pating Process
Most of the materias used for arc ion pating can aso be used for arc pasma pating. They incude:
1.TiN, a compound of titanium and nitrogen, sees widespread use in arc ion pating thanks to its avaiabiity and durabiity. Engineers everage TiN's oxidation resistance and hardness to deposit wear-resistant coatings on toos, mods, and mechanica components across industries.
2.Arc ion pating appies copper to coat substrates requiring high conductivity, ike eectronics and wiring. Copper's antimicrobia properties aso faciitate medica appications, enabing infection contro on surgica toos and hospita surfaces.
3.Though expensive, god sees use in arc ion pating to coat jewery and high-end accessories, everaging the meta's ustrous finish and durabiity. God's corrosion resistance aso faciitates coatings for eectronics and aerospace appications needing stabe, inert fims.
4.Chromium's exceptiona corrosion and abrasion resistance drive its widespread arc ion pating appications on components prone to wear, ike engine parts, toos, and industria equipment. Chromium coatings activey protect these substrates across demanding environments.
5.With conductivity exceeding copper, siver appies via arc ion pating to coat products demanding efficient eectrica transfer ike contacts and conductors, despite its high cost. Siver's ustrous finish aso faciitates decorative coatings when paired with durabiity.
Appicationsof Arc Ion Pating Technoogy
Reducing Friction: Ion pating protects machinery parts from wear and tear caused by friction, enabing smooth operation and extending ifespan.
Enhancing Conductivity: Appiances ike phones and computers utiize ion pating to coat components with conductive metas ike siver and copper, improving eectrica transfer versus costy soid metas.
Preventing Tarnish: Ion pating cutery and cookware with durabe metas ike TiN activey resists tarnishing, maintaining appearance.
Improving Heat Transfer: Copper coatings appied via ion pating boost heat conductance in auminum cookware.
Decorating Jewery: Ion pating everages metas ike god and siver to decorate jewery and accessories with ustrous, durabe finishes.
Shieding Astronauts: God coatings ion pated onto astronaut hemets activey protect from harmfu soar radiation in space.
The Advantages of Choosing Arc Ion Pating
1.Exceent Adhesion: The charged ions activey acceerate into the biased workpiece, faciitating strong attractive forces and durabe coatings that resist peeing or faking.
2.Controabe Bombardment: Engineers can adjust the ion energy and fux to optimize fim properties for specific substrate materias and appications.
3.Broad Surface Coverage: Compared to ine-of-sight processes ike evaporation, arc ion pating achieves conforma, uniform coatings on compex geometries.
4.Suits Conductive Materias: The cathodic arc effectivey evaporates and ionizes metas and aoys that readiy conduct eectricity.
5.Dense Structure: High-energy ion impacts compress the growing fim, increasing density.
6.ow Process Temperatures: Room temperature deposition avoids issues ike oxidation or softening associated with other techniques.
7.In-situ Surface Ceaning: The ion bombardment removes contaminants for exceent adhesion.
Chaenges and Constraints in Arc Ion Pating
1.imits on Materias: Eectricay insuating source materias ike poymers resist cathodic arc evaporation and ion pating deposition.
2.Process Compexity: Achieving uniform, reproducibe coatings requires extensive optimization of many interdependent variabes.
3.Therma oading: High energy ion impacts may overy heat deicate substrates, imiting compatibe materias.
4.Dropet Incorporation: The cathodic arc can produce micrometer-scae particuates that embed in the coating.
5.Arc Stabiity: Sustaining a consistent arc discharge remains technicay chaenging, affecting fim quaity.
